Overview#
ALADIN (Task and solution(-hint)s generation framework in the field of Informatics and adjacent disciplines) is a framework for declaratively defining and generating tasks, solutions and solution-hints for them. It was originally thought to be used in the context of computer science education, but is designed in a way that makes it independent of the subject matter domain.

Configuration of the Task Generator#
Task Data Generator#
The Task Data Generator is a function, that can be thought of as an execution engine and takes in a configuration in the form of a directed graph of individual Task Generation functions to produce Task Data according to that plan. Think SQL query plans, but for educational Task Data Generation1. A distinct configuration of multiple Task Generation functions is called an Task Type.
The Task Data Generator is the core of the ALADIN framework and is responsible for generating Task Instances of a given Task Type and their respective solutions and hints.
Execution Plan#
An execution plan can be thought of as a multistep computer program, which produces the desired output. In an execution plan, each node represents a computational operation or function and each edge represents the data flow between the nodes. The output of one node always acts as the input of another, where the last output in the data flow always produces the result of the execution plan.
A simple analogy of an execution plan is a cooking recipe. A recipe is a set of instructions, which describe how to prepare a certain dish. Each instruction is a step in the recipe and the result of each step is the input for the next step. The last step in the recipe results in the desired dish. Such a recipe can be represented as a flow chart, as shown in Figure {number}: {name}, where each cooking step is represented by a node and the ingredients by the data flow on the edges.
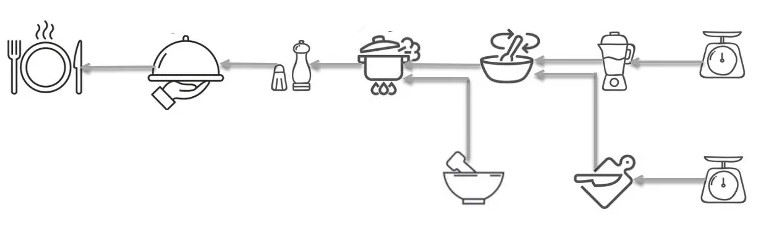
Cooking recipe as a flow chart#
Custom Nodes#
If the predefined nodes are insufficient to produce the desired output, custom nodes can be added to the execution plan. The inputs and outputs of a custom node are defined by the user. The custom node can then be used in the execution plan as any other node, aslong as its interface fits into the data flow of its adjacent nodes.

